Introduction
If you’ve ever experienced itchy, inflamed skin, you might be dealing with ringworm or eczema. Both conditions can be quite uncomfortable and confusing. So, what exactly causes these skin issues, and what are the risk factors involved? In this article, we’ll dive deep into the causes and risk factors of ringworm and eczema, helping you understand these conditions better and offering some tips for prevention.
What is Ringworm?
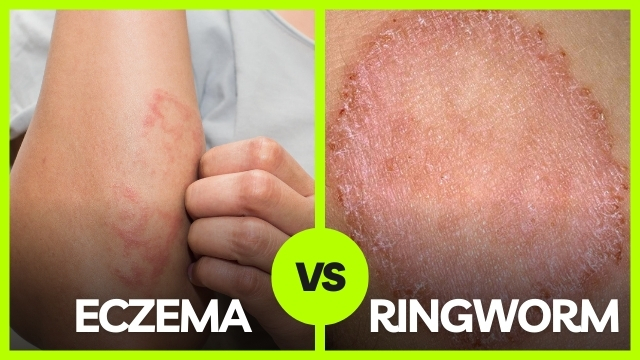
Ringworm, despite its name, isn’t caused by worms but by a fungal infection. It’s a common skin condition that causes a circular, red, itchy rash. The rash often has a raised, scaly border and can appear anywhere on the body.
Symptoms of Ringworm
The primary symptoms of ringworm include:
-
Itchy Skin: The affected area is usually very itchy.
-
Circular Rash: Look for a red, ring-shaped rash with a clear center.
-
Scaly Skin: The rash may be scaly or crusty.
What is Eczema?
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a condition that makes your skin red, inflamed, and itchy. It’s not just a single skin issue but a term that encompasses several types of dermatitis.
Symptoms of Eczema
Typical symptoms of eczema include:
-
Dry, Itchy Skin: The skin often feels dry and itchy.
-
Red, Inflamed Patches: These patches can appear on various parts of the body.
-
Thickened Skin: Over time, the skin may become thickened due to frequent scratching.
Causes of Ringworm
Understanding the causes of ringworm can help you take steps to avoid it.
Fungal Infection
Ringworm is caused by fungi called dermatophytes. These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments, making it easy for them to infect the skin. They can spread through direct contact with an infected person, animal, or contaminated surfaces.
Environmental Factors
The environment plays a significant role in the spread of ringworm. Warm, humid conditions are perfect for fungi to grow and spread. So, if you’re often in such environments, be extra cautious.
Risk Factors for Ringworm
Certain factors can increase your likelihood of contracting ringworm.
Weakened Immune System
People with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to fungal infections, including ringworm. If your immune system is compromised, you might be more likely to catch ringworm.
Close Contact with Infected Individuals
Ringworm is highly contagious. Close contact with someone who has ringworm can easily spread the infection. This includes physical contact or sharing personal items like towels and combs.
Causes of Eczema
Eczema is often a result of a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Genetic Factors
Genetics play a crucial role in eczema. If you have a family history of eczema or other allergic conditions like asthma, you’re more likely to develop eczema yourself.
Environmental Triggers
Various environmental factors can trigger eczema flare-ups. These include harsh soaps, allergens, and changes in temperature or humidity. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help manage eczema symptoms.
Risk Factors for Eczema
Understanding the risk factors can help you prevent eczema or manage it more effectively.
Family History
If your family has a history of eczema, allergies, or asthma, you’re at a higher risk of developing eczema. It’s one of the key risk factors for this condition.
Skin Irritants and Allergens
Exposure to skin irritants and allergens can trigger eczema flare-ups. Common culprits include certain fabrics, detergents, and environmental allergens like pollen or pet dander.
Comparison of Ringworm and Eczema
While ringworm and eczema both affect the skin, they have distinct differences and some similarities.
Similarities
Both conditions can cause itchy, inflamed skin. They can also be triggered or worsened by environmental factors.
Differences
The primary difference is the cause: ringworm is caused by a fungal infection, whereas eczema is often related to genetic and environmental factors. Ringworm typically appears as a ring-shaped rash, while eczema presents as dry, inflamed patches.
Prevention Tips
Preventing ringworm and eczema involves a combination of good hygiene and avoiding triggers.
-
For Ringworm:
-
Keep your skin clean and dry.
-
Avoid sharing personal items.
-
Use antifungal treatments if necessary.
-
-
For Eczema:
-
Moisturize your skin regularly.
-
Avoid known irritants and allergens.
-
Wear soft, breathable fabrics.
-
Conclusion
Both ringworm and eczema can cause significant discomfort, but understanding their causes and risk factors can help you manage and prevent these conditions more effectively. By following the tips and being aware of the triggers, you can reduce the risk of flare-ups and keep your skin healthy and comfortable.
FAQs
1. Can ringworm be treated at home?
Yes, ringworm can often be treated at home with over-the-counter antifungal creams. However, if it persists or spreads, consulting a healthcare professional is advisable.
2. What is the best way to prevent eczema flare-ups?
Keeping your skin moisturized with moisturizing cream, avoiding known irritants, and managing stress can help prevent eczema flare-ups.
3. Are ringworm and eczema contagious?
Ringworm is contagious and can spread through direct contact or contaminated surfaces. Eczema is not contagious.
4. How can I tell if I have ringworm or eczema?
Ringworm typically presents as a circular rash with a clear center, while eczema appears as dry, inflamed patches on the skin. If unsure, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
5. Can diet affect eczema?
Yes, certain foods can trigger eczema flare-ups in some people. Keeping a food diary and avoiding known triggers can help manage symptoms.